
Power point slide of the above picture: Network.ppt
Subsystems
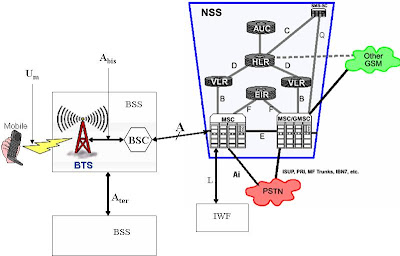
Network Switching System (NSS)
The Network Switching System (NSS) or simply the switching system (SS) is responsible for performing call processing and subscriber-related functions. The switching system includes the following functional units:
- home location register (HLR)-The HLR is a database used for storage and management of subscriptions. The HLR is considered the most important database, as it stores permanent data about subscribers, including a subscriber's service profile, location information, and activity status. When an individual buys a subscription from one of the *mobile services switching center (MSC)-The MSC performs the telephony switching functions of the system. It controls calls to and from other telephone and data systems. It also performs such functions as toll ticketing, network interfacing, common channel signaling, and others.
- visitor location register (VLR)-The VLR is a database that contains temporary information about subscribers that is needed by the MSC in order to service visiting subscribers. The VLR is always integrated with the MSC. When a mobile station roams into a new MSC area, the VLR connected to that MSC will request data about the mobile station from the HLR. Later, if the mobile station makes a call, the VLR will have the information needed for call setup without having to interrogate the HLR each time.
- authentication center (AUC)-A unit called the AUC provides authentication and encryption parameters that verify the user's identity and ensure the confidentiality of each call. The AUC protects network operators from different types of fraud found in today's cellular world.
- equipment identity register (EIR)-The EIR is a database that contains information about the identity of mobile equipment that prevents calls from stolen, unauthorized, or defective mobile stations.
The AUC and EIR are implemented as stand-alone nodes or as a combined AUC/EIR node.
Base Station System (BSS)
All radio-related functions are performed in the BSS, which consists of base station controllers (BSCs) and the base transceiver stations (BTSs).
- BSC-The BSC provides all the control functions and physical links between the MSC and BTS. It is a high-capacity switch that provides functions such as handover, cell configuration data, and control of radio frequency (RF) power levels in base transceiver stations. A number of BSCs are served by an MSC.
- BTS-The BTS handles the radio interface to the mobile station. The BTS is the radio equipment (transceivers and antennas) needed to service each cell in the network. A group of BTSs are controlled by a BSC.
Operation and Support System (OSS)
The operations and maintenance center (OMC) is connected to all equipment in the switching system and to the BSC. The implementation of OMC is called the operation and support system (OSS). The OSS is the functional entity from which the network operator monitors and controls the system. The purpose of OSS is to offer the customer cost-effective support for centralized, regional, and local operational and maintenance activities that are required for a GSM network. An important function of OSS is to provide a network overview and support the maintenance activities of different operation and maintenance organizations.
Additional Functional Elements
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Other functional elements shown are as follows:
- message center (MXE)-The MXE is a node that provides integrated voice, fax, and data messaging. Specifically, the MXE handles short message service, cell broadcast, voice mail, fax mail, email, and notification.
- mobile service node (MSN)-The MSN is the node that handles the mobile intelligent network (IN) services.
- gateway mobile services switching center (GMSC)-A gateway is a node used to interconnect two networks. The gateway is often implemented in an MSC. The MSC is then referred to as the GMSC.
- GSM interworking unit (GIWU)-The GIWU consists of both hardware and software that provides an interface to various networks for data communications. Through the GIWU, users can alternate between speech and data during the same call. The GIWU hardware equipment is physically located at the MSC/VLR.
Protocols

The Base Station Application Part (BSAP) is the application layer signaling protocol that provides messaging to accomplish the functions of the A1 Interface component of the MSC - BS Interface. BSAP is split into two sub-application parts; the BS Management Application Part (BSMAP), and the Direct Transfer Application Part (DTAP).
The BS Management Application Part (BSMAP) supports all Radio Resource Management and Facility Management procedures between the MSC and the BS, or to a cell(s) within the BS. BSMAP messages are not passed to the MS, but are used only to perform functions at the MSC or the BS. A BSMAP message (Complete Layer 3 Information) is also used together with a DTAP message to establish a connection for a MS between the BS and the MSC, in response to the first layer 3 air interface message sent by the MS to the BS for each MS system request. The description of the layer 3 protocol for the BSMAP information exchange is contained within this specification.
The Direct Transfer Application Part (DTAP) messages are used to transfer call processing and mobility management messages between the MSC and BS. DTAP messages carry information that is primarily used by the MS. The BS maps the DTAP messages going to and coming from the MSC from/into the appropriate air interface signaling protocol.
Terms/Abbreviations
IMSI - International Mobile Subscriber Identifier. Wikipedia page: IMSI
ESN - Electronic Serial Number. Wikipedia Page: ESN
ESNs are mainly used with AMPS and CDMA phones in the United States, compared to IMEI numbers used for GSM phones in Europe and elsewhere.
MDN - Mobile Directory Number
CIC - Circuit Identification Code
IS-41 (ANSI-41)
ANSI-41 (IS-41) is a standard for identifying and authenticating users, and routing calls on mobile phone networks. The standard also defines how users are identified and calls are routed when roaming across different networks.
ANSI-41 is the standard used by AMPS (analog), IS-136 (TDMA) and CDMA networks.
GSM and WCDMA networks use a different standard, known as MAP.
CMSR - Connection Management Service Request
Few important points
- In case of mobile cic is chosen by MSC and sent to the BSC.
- In case of ISUP cic come in the IAM megssage
Subscriber Registration
TBD
Mobile to mobile call (M-M Call flow)
TBD
Mobile to PSTN Call
TBD
PSTN to Mobile Call
TBD
